Contact us directly to discuss your specific requirements, help you with purchasing, or with any other questions.
This "how-to-connect" documentation will explain the initial configuration of an example connection from Azure Blob container to a SharePoint Document library.
This guide presupposes that you have installed the Layer2 Cloud Connector and that you are familiar with its basic functionality. The Layer2 Cloud Connector User Documentation will provide you with all necessary information.
Move your storage from SharePoint Online to Azure Blob Storage. Let SharePoint, Teams and OneDrive users work in all three systems as usual - users can retrieve archived data with just one click.
To access your Microsoft Azure container with the Layer2 Cloud Connector you must get Azure Storage account connection string. Please select the desired Azure storage account and under the settings are click on Access keys, you will see that you can reveal the storage keys as shown below:
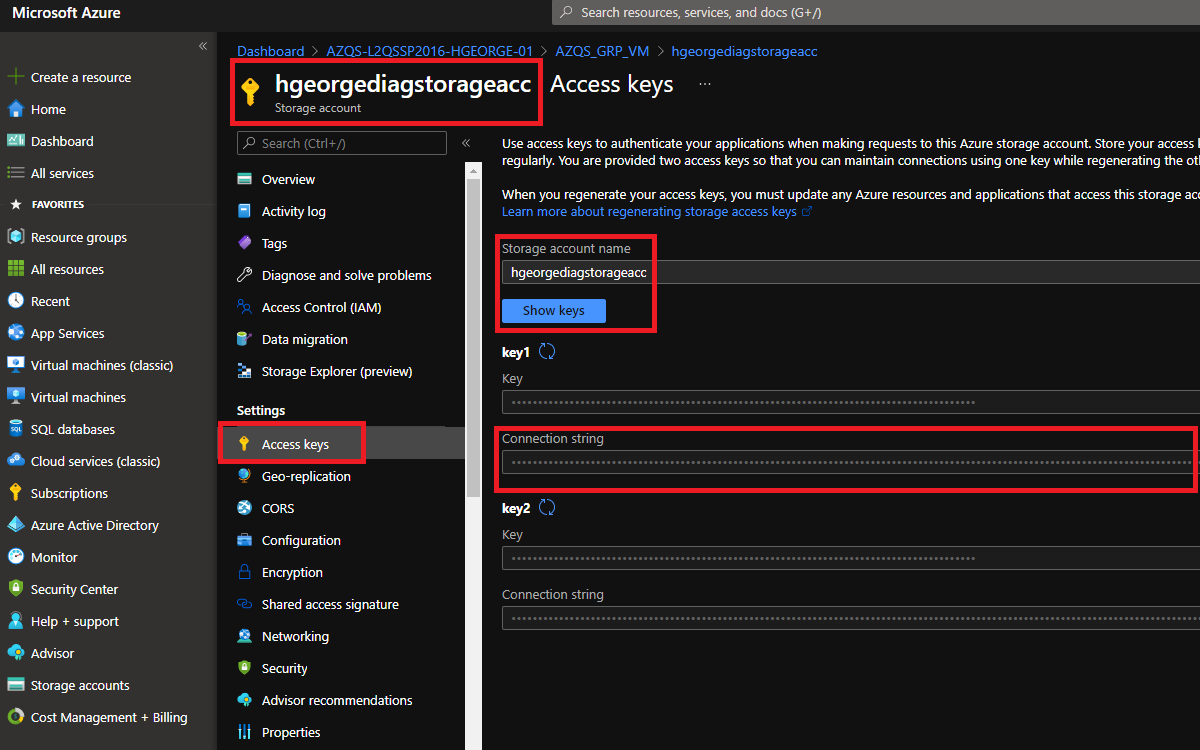
Once the keys are revealed, please copy one of the two connection strings provided and paste it in a local file. We must add your container name to your connection string.
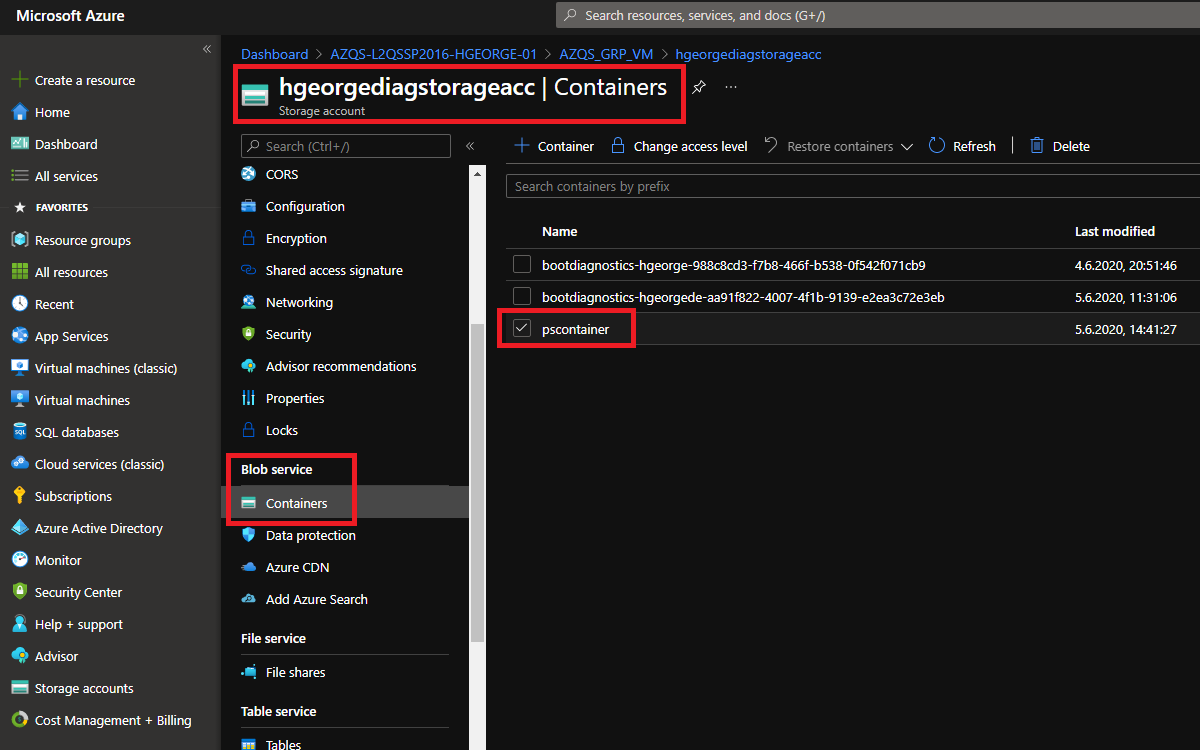
Now we must select the storage container where we will get the data from. Please go to your Storage account, find the Blob Service area and select Containers. Once there, please copy the container name that the Layer2 Cloud Connector will be working on. We need the container name for the connection string.
Create a new connection by using the Create New Connection option in the Actions pane (right-hand side). The new connection will appear at the bottom of the Connection Manager List (left-hand side). Click on your newly created connection to open the connection configuration settings.
Choose a meaningful name for your connection and replace the current "New Connection" Connection Title with it.
The Connection can be bi-directional. An initial connection should always be uni-directional to assure that both data entities are identical before switching to bi-directional. Therefore, choose Left to Right as Direction. You can change this setting after your initial synchronization finished successfully.
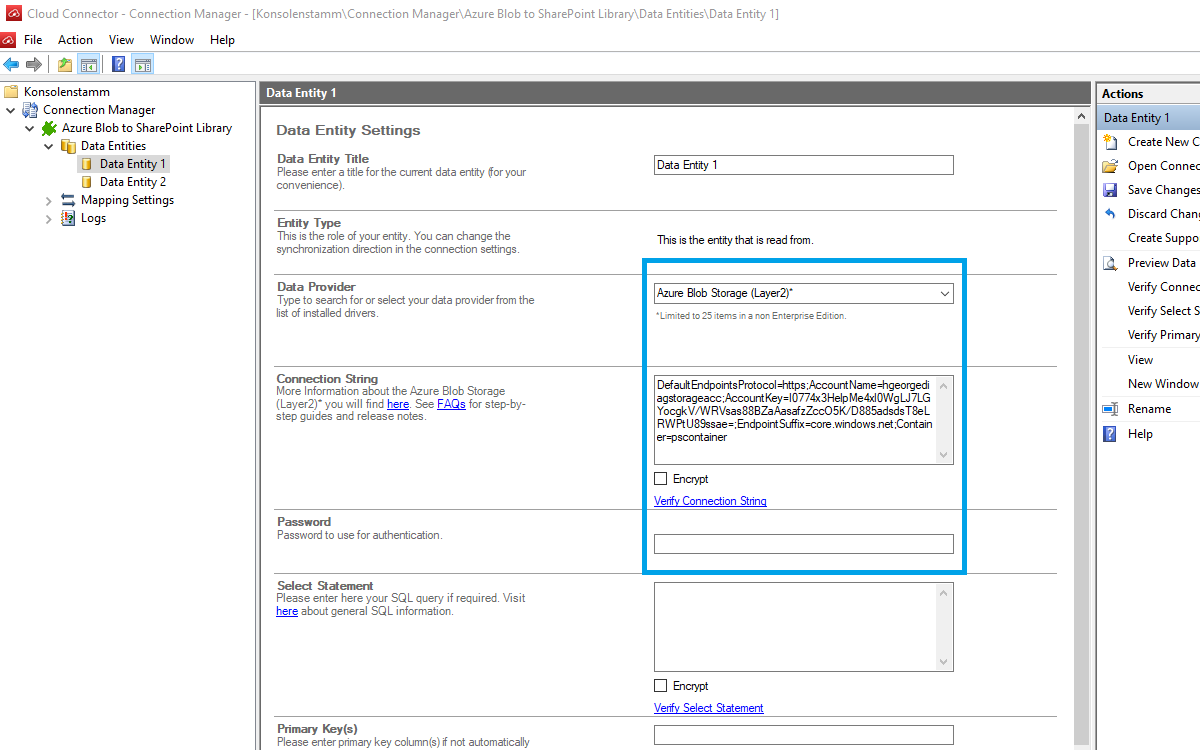
We will now set up our Data Entities. Go to the data entity “Data Entity 1” to open the configuration settings.
Select the Provider for Azure Blob Storage (Layer2) from the data provider list. You can search for Azure Blob Storage by typing into the selection box.
For the Connection string, we need the storage account connection string and container name information mentioned in step 1. You can copy the connection string below and adjust it to match your information.
Connection String:
DefaultEndpointsProtocol=https;
AccountName=hgeorgediagstorageacc;
AccountKey=I077Ug9gfhjhjrsHelpMeJ7LGYocgkV/WRV2erEEGC7BzugzZccO5K/Djdsgfg69AT8eLRW55PtUds;
EndpointSuffix=core.windows.net;
Container=pscontainer
Use the Verify Connection String option to evaluate if the provided connection string is valid.
To check if all necessary columns are received, you can use the Preview Data option on the right-hand pane which will provide you with a pop-up window showing the data from your Document Library.
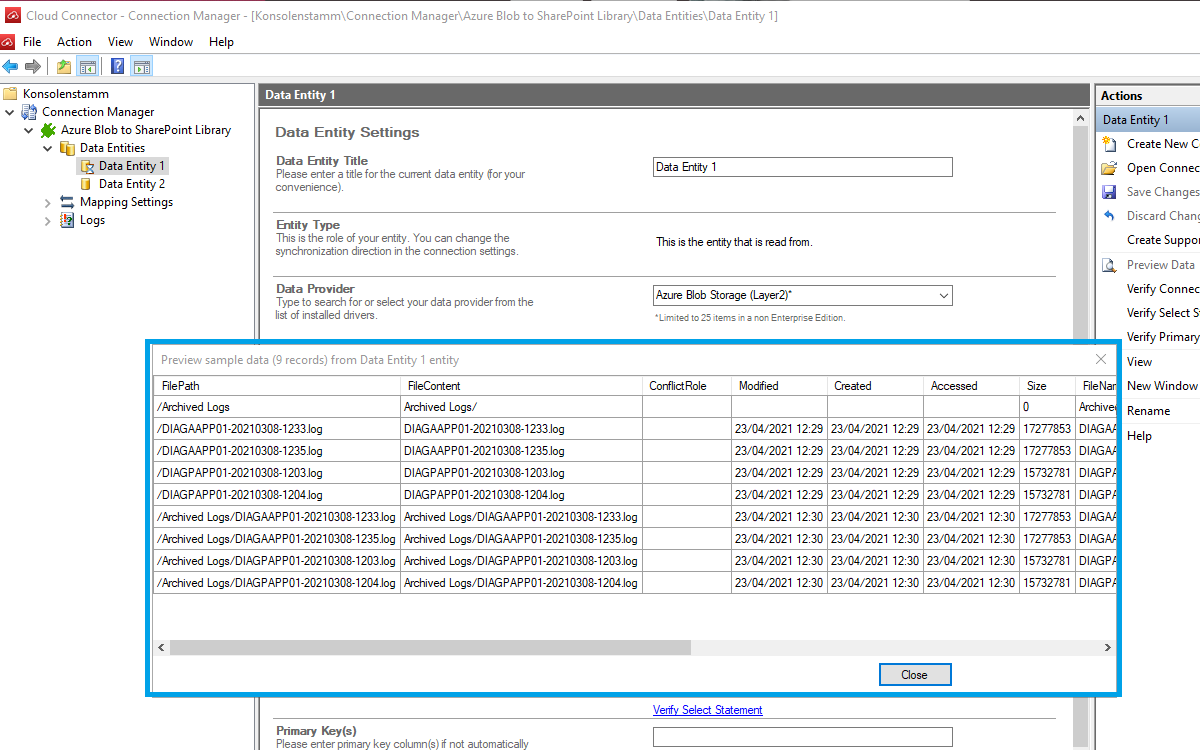
Now we are going to send the data to the destination Document Library on your SharePoint Online. It's required that you set up this library prior to the next steps. Your library should contain matching columns according to your source entity.
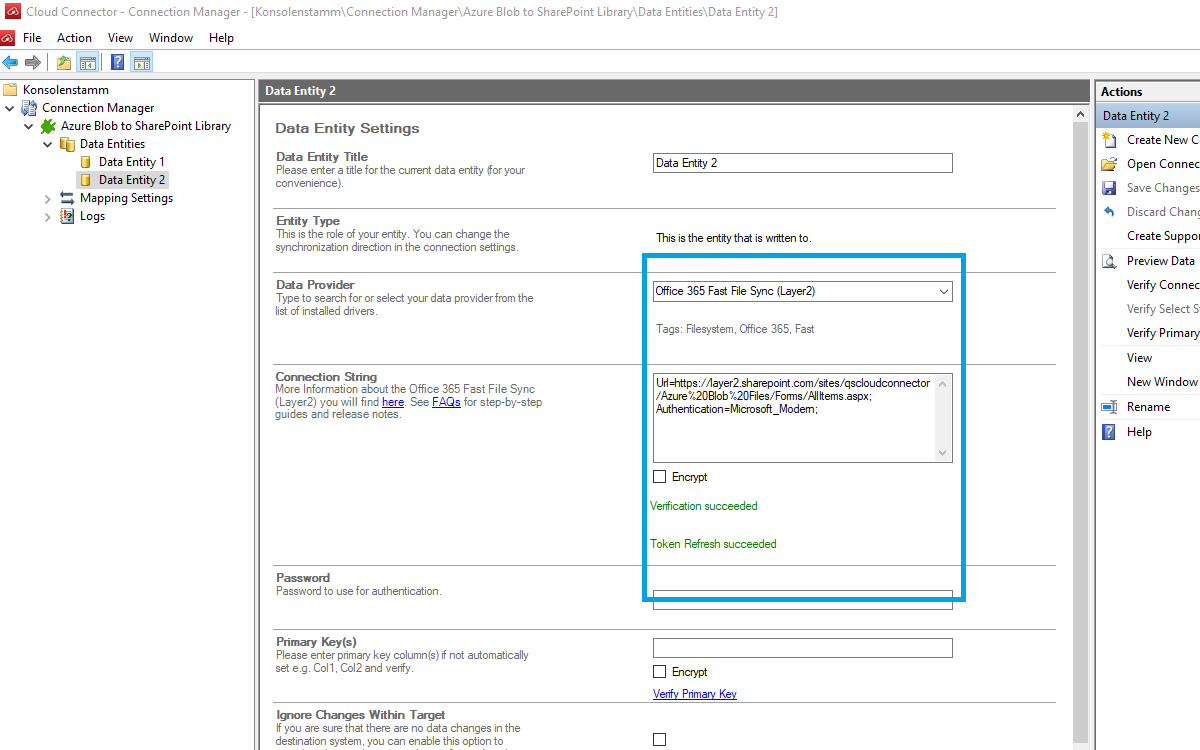
Use the left-hand pane to switch to the data entity "Data Entity 2". We will be using the Layer2 SharePoint Provider as well.
For more information about the SharePoint provider please visit Layer2 SharePoint provider Specification.
You can copy the below Connection String which contains the minimum of required properties to connect to your custom SharePoint Online Document Library.
Connection String:
Url=https://myTenant.sharepoint.com/sites/mySite/myLibrary/Forms/AllItems.aspx;
Authentication=Microsoft_Modern;
Save your changes by using the right-hand pane option Save Changes.
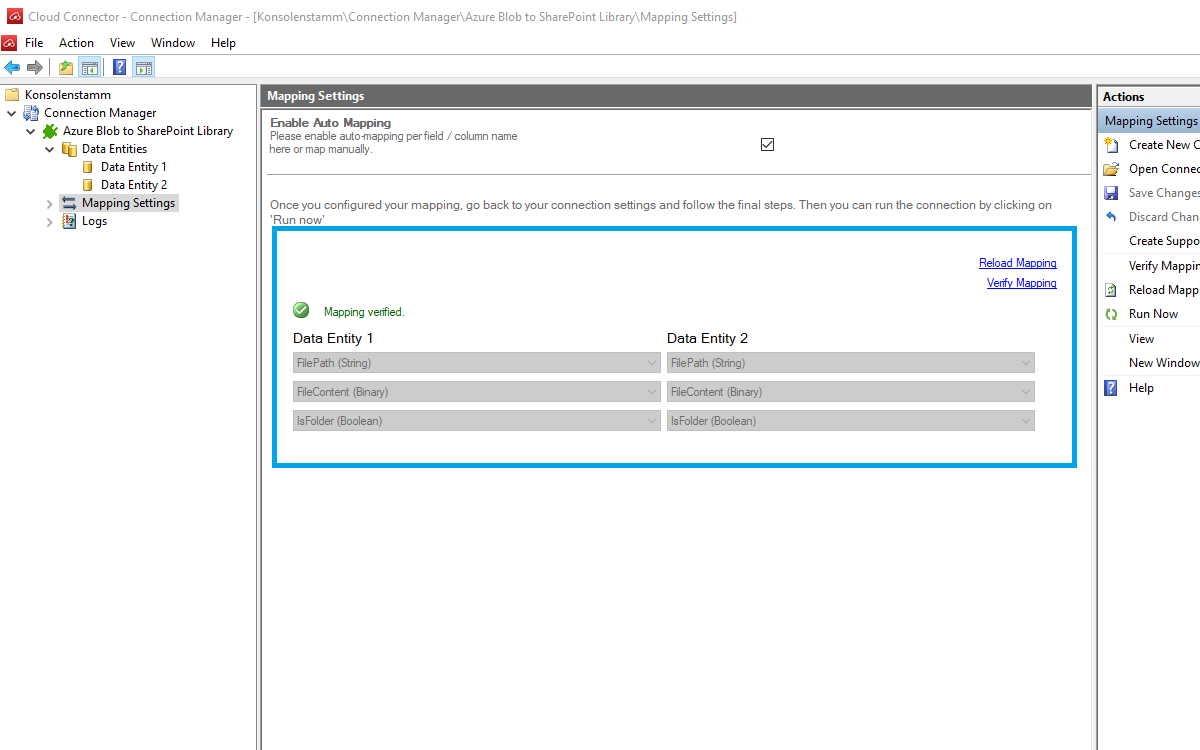
In the next step, we will configure our mapping settings. Click on the Mappings option on the left-hand pane.
If your fields from SharePoint are named identical to the fields from your source system, the Enable Auto Mapping option will match those columns. Disabling this option allows you to match your columns as needed.
We enabled auto-mapping in our setup. Save your changes by using the right-hand pane option Save Changes.
To run your connection switch back to the main connection configuration node and use the Run Now Button located on the bottom of the setup page. The Run Synchronization Toolbox will also display the synchronization process.
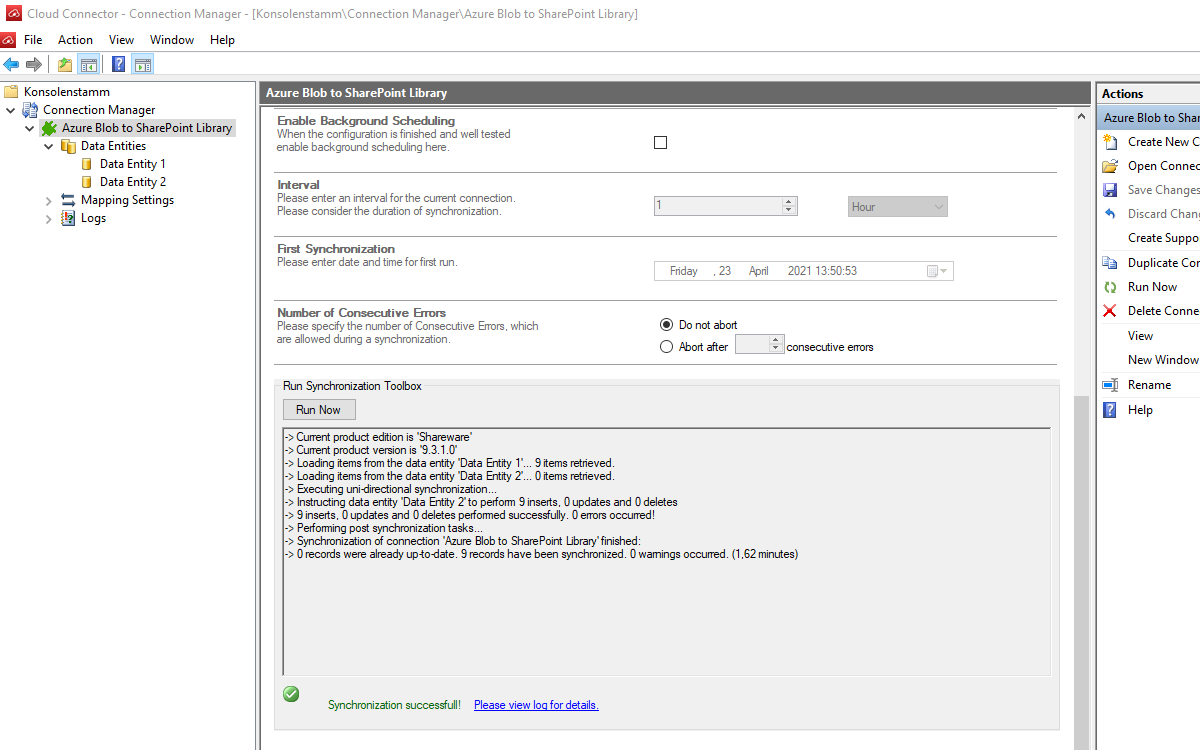
This will be the result in our SharePoint Online library after our initial successful synchronization:
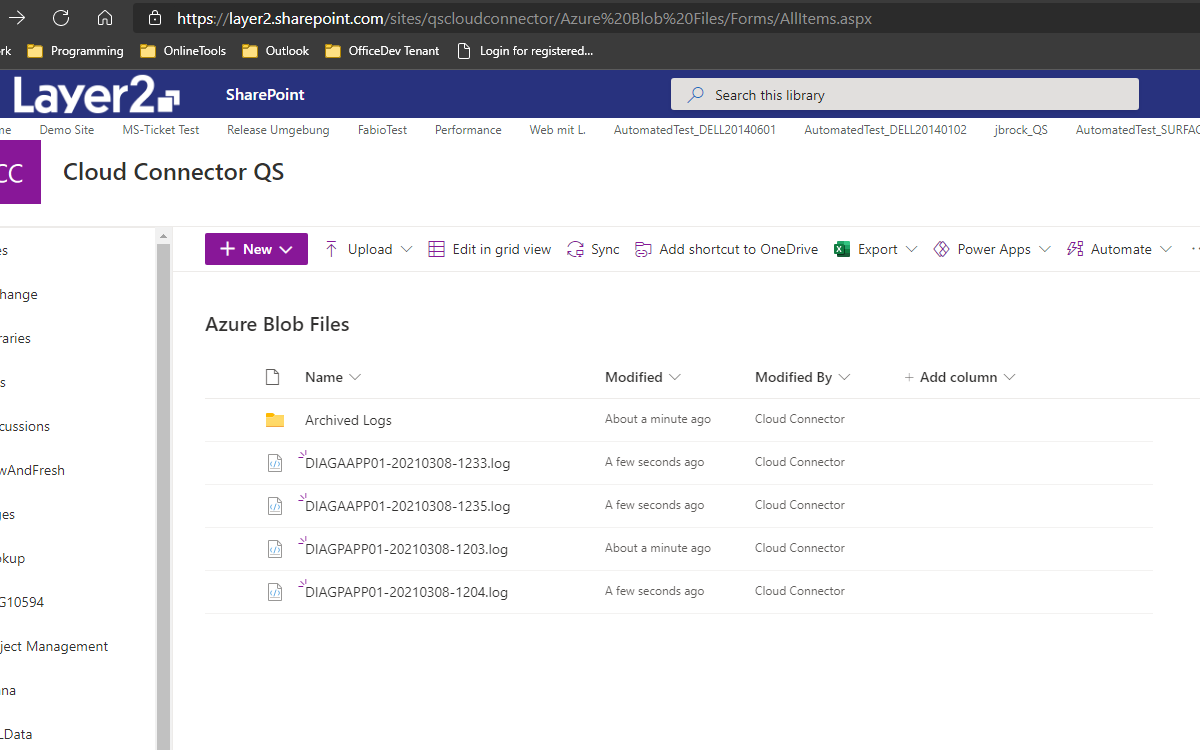
If you want to use a bi-directional synchronization, you can now switch your connection direction after our initial synchronization finished successfully.
After adjusting the direction, you should check your Mappings settings again because some systems might include read-only columns that cannot be mapped directly.
We also recommend to choose a Conflict Resolution that matches your environments needs.
You can find out more about the different conflict resolutions in our Layer2 Cloud Connector User Documentation.
Azure Blob Storage is a flat virtual file system without folder hierarchy. The folder hierarchy that is built in the UI is virtual and based on blob name prefixes. So in case a blob is named “myPrefix/mySuffix”, it will be represented by a folder named “myPrefix” and a blob inside this folder with name “mySuffix”. Therefore it is not possible to create empty folders in Azure Blob Storage.
The Cloud Connector handles this as if the empty folder would exist in the blob storage. However, if you check your Azure Blob Storage container, it will not contain empty folders even if the Cloud Connector reports and treats them as being created.
In case the connection string parameter FileReadMode is set to Flat after the initial sync, the full folder hierarchy in the Azure Blob container will still be provided (but without the files in sub folders).
The connection string parameter IncludeFolders should only be set to false before the initial sync. Otherwise, the Cloud Connector will always provide all folders from the Azure Blob container.